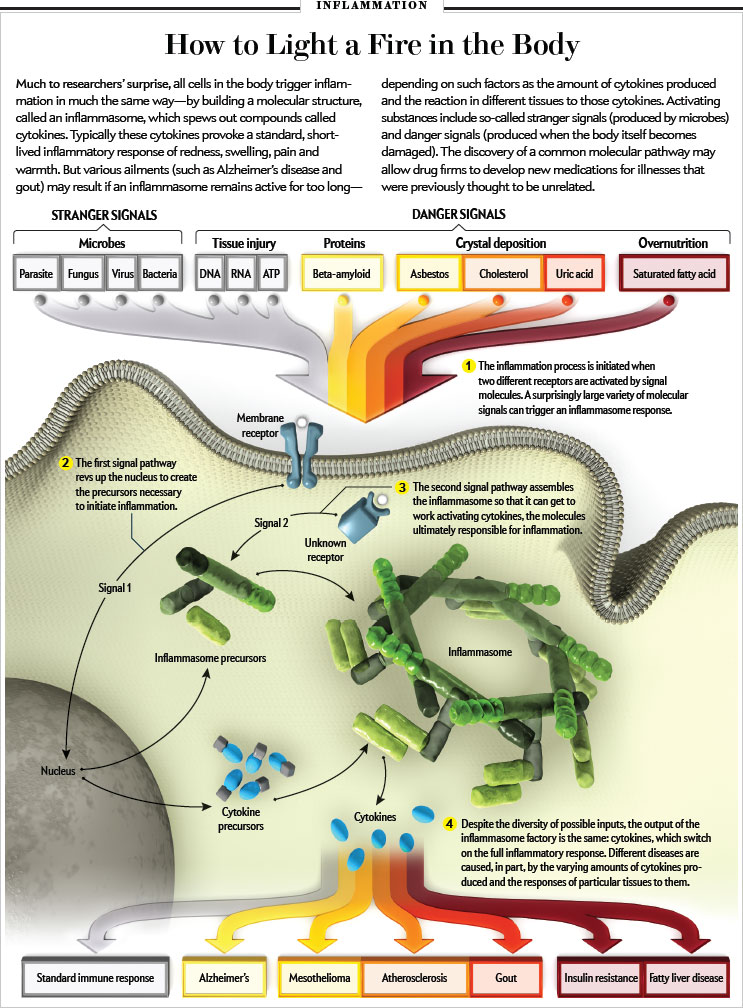
Neuroinflammation in Psychiatry
Neuroinflammation Definition: an organism attempts to remove an injurious stimulus in the central nervous system (CNS) and initiates a healing process to protect the brain.
It also comprises responses by microglia see (microglia synopsis), the resident CNS immune cells, increasing inflammatory signals activating immune responses of the CNS. This response can be both protective and toxic, and it can trigger acute and chronic brain changes. Neuroinflammation is a common feature in most severe Psychiatric Illness, Brain damage and Medical Illness. In pregnancy it is a major risk factor for neuro-developmental disorders.
Neuroinflammation and Psychiatric Conditions: Neuroinflammation is a factor in many psychiatric illnesses, such including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorders and Schizophrenia, but also neuro-degenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease and Neuro-developmental diseases such as ADHD and Autistic Disorders.
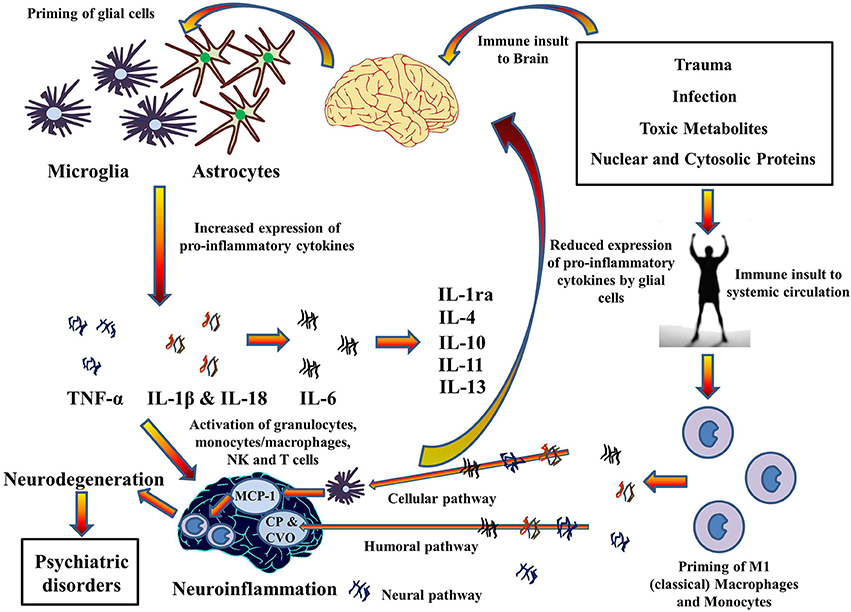
Inflammatory levels of cytokines are found in depression, schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s Disease. High levels of CRP (C-Reactive Protein) in the brain have been linked to neuroinflammation and associated cognitive impairment and dementia, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Chemokines promote neuroinflammation by attracting leucocytes to the point of inflammation. Neuroinflammation in turn has been implicated for the impairment of brain function. TNF-α and IL-1 cytokines, are pro-inflammatory cytokines that have been primarily implicated in neuroinflammation causing a reduction in hippocampal volumes through the neurodegenerative TNFR1 pathway and can lead to the development of depressive-like behavior. Glial cells, microglia, and astrocytes, are the primary immune effector cells and express various cytokines in the CNS. Though glial cells are neuroprotective, their over expression or sustained stimulation results in increased levels of cytokines, which may cause cellular damage.
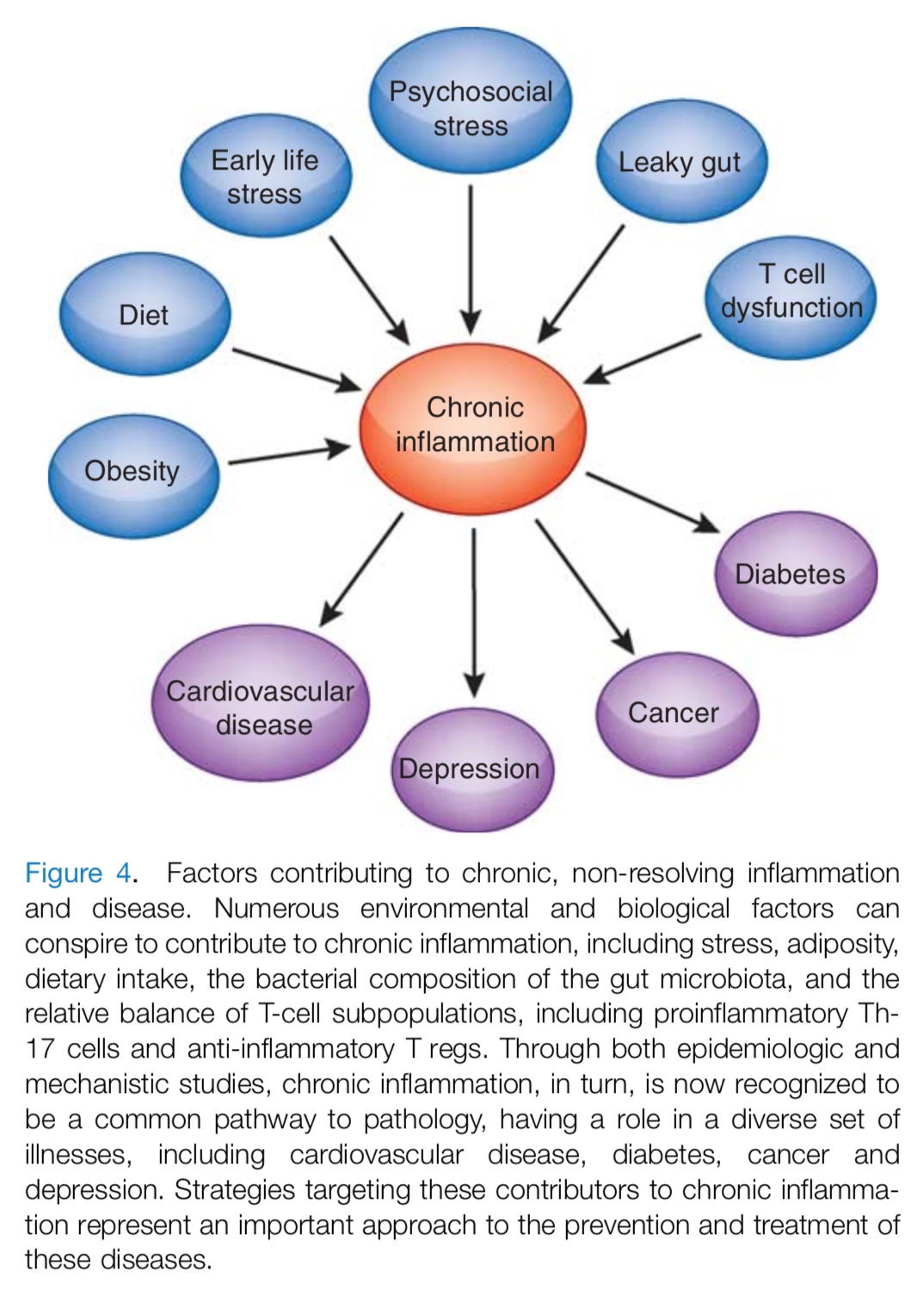
Neuro-inflammation and Medical Conditions: Numerous environmental and biological factors conspire to contribute to chronic inflammation, including life stressors, obesity, food intake, the bacterial composition of the gut microbiota, and the relative balance of T-cell subpopulations. Chronic inflammation, in turn, is a common pathway to multiple medical illnesses, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer and fibromyalgia. This understanding may help to lead to newer prevention and treatment strategies for these diseases.
Infographic: Scientific American 0615-44-I3
Lifetime Factors contributing to chronic inflammation
Holistic Top 10 Strategies to Prevent Neurone-degeneration:
A Holistic Treatment Approch is based on understanding how Microglia activated by major psychiatric and medical Disorders, involving psychosis, anxiety, and pain, increase neuro-inflammation. This results in a cascade that releases inflammatory cytokines and free radicals which cause degenerative brain changes and apoptosis.
- Absolute Adherence to Antipsychotic Treatment, preferably by long acting IM injection to maintain adequate and steady state levels of antipsychotic medication which reduces neuro-inflammatory processes.
- Use of Second Generation Atypical Antipsychotics which target multiple neurotransmitters other than dopamine and stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which have been shown to be protective of neurogenesis.
- Use of SSRI antidepressants for depression and anxiety, but which also stimulate neurogenensis.
- Use of Mood Stabilizers, particularly Lithium, Valproate, and Lamotrigen, which elevate rain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), reduce Glutamate and are strongly neuroprotective
- Use of an anti-inflammatory agent such as ASA, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, a COX-2 inhibitor, or minocycline.
- Use of an adjunctive strong antioxidant, such as N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) a precursor of Glutathione, a neuro-protective agent.
- Use of Omega-3 Supplements and Lithium, that inhibits Caspase-3, which causes neuro-inflammation and apoptosis (neuronal death) during psychosis.
- Avoid use of Recreational Drugs that stimulate Dopamine excess and increase neuro-inflammation, such as Cocaine, Amphetamines and Cannabis.
- Hope for future drugs that target Glutamine excess such as Bitopertin or Antagonists of LINGO-1, a negative regulator of axonal myelination.
- Improve general health, physical activity, exercise, avoid obesity, stop smoking, all of which reduce inflammatory cytokines and free radicals.
References:
- Only One Neurobiologic Disorder: H.Nasrallah 2015 The Case for Inflammation as the Common Element.
- Brain Repair Tactics in Schizophrenia: H.Nasrallah 2015 Beyond the Dopamine Theory: Strategies How to Prevent Neurodegeneration
- Inflammatory Cause of Bipolar Disorder: Zoler et al 2011 Article suggests new treatments.
- Bipolar Disorder: Role of Inflammation and Bio Markers.
- Neuroprogression to Neuroprotection: Berk et al 2010 Article reviews treatments efficacy.
- NAC Therapy: Berk et al 2010 Article Re NAC (N-acetylcysteine) useful in mood disorders.
- Cytokines in Major Depression: Miller et al 2009 Review Article
- Inflammation and Treatment Resistance in MDD: H.Miller et al 2013 Review Article.
- Psycho-neuroimmunology and Neuro-psychopharmacology: Impact of Inflammation on Behavior: H.Miller et al 2012: Complex Review Article on the Mind – Body connect. See above Fig.
- Are Microglia the Most Intelligent Brain Cells?: Jon Lieff PhD. 2013 Graphic Summary Article
- Inflammasomes and Brain Function: Frontiers in Neuroscience 2014.
- Microglia Synopsis: Journals & Books: Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases